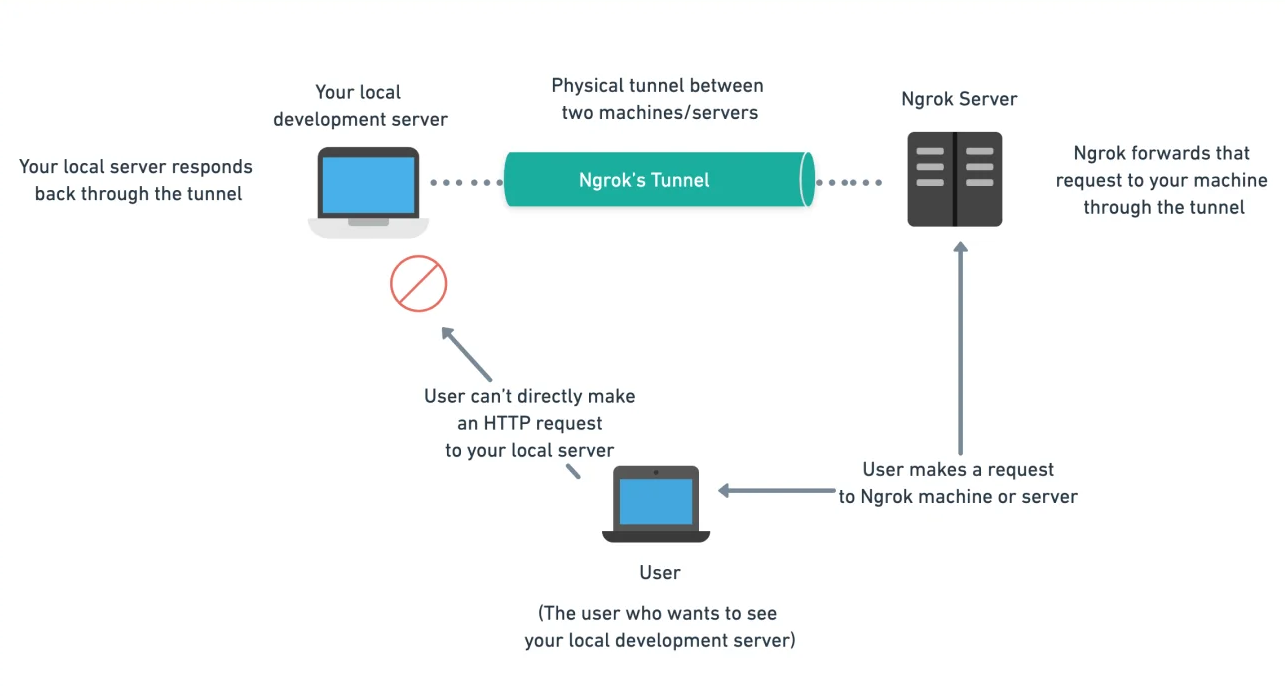
We are in the 4.0 era and smartphones are an indispensable device in daily life. Smartphones today are present in every area of human life. They come from many different brands, but if classified by operating system, there are two popular platforms: Android and iOS.
Apple was the first company to bring the concept of the modern touchscreen smartphone to consumers, and the iPhone's market share has declined significantly since it was first introduced.
In 2010, Android surpassed iOS in market share, becoming the most popular mobile operating system in the world. It's a title that Android still holds to this day. And although some may argue about which operating system is better, there is no denying which operating system is more popular as Android maintains over 80% of the global market share.
Why are Android phones more popular than iPhones?
1. More and more smartphone manufacturers are using Android
In 2007, Google and several mobile operators, software companies, and hardware companies formed the Open Handset Alliance (OHA) to compete with the launch of the iPhone. This alliance established Android as the mobile platform of choice, granting open-source licenses to manufacturers. It is this factor that makes more and more smartphone and device manufacturers use Android as the operating system for their devices. In contrast, IOS is limited to iPhones and iPads manufactured by Apple.
Additionally, regional brands and new startup manufacturers are also adopting this operating system. The boom in demand for smartphones in the Chinese and Indian markets has meant that local companies' adoption of Android has enhanced their global share of the smartphone market. Several other mobile operating systems continue to try to compete with Android and IOS like Windows Phone or Symbian.
However, when these companies failed to gain a significant foothold in the market, their smartphone brands eventually switched to Android. In fact, in the Vietnamese market, all phone companies currently use the Android operating system, and only Apple uses the iOS operating system. Android dominates in both the number of manufacturers and the number of phones produced during the year.
For example, Samsung can make up to 20 phone lines in 1 year spanning different price segments, while Apple only makes 4-5 phone lines.
2. Android devices cover a wide range of price segments
One reason why the Android operating system is more popular than iOS is because of the diverse prices of Android devices. This is extremely important for countries with developing economies and weak USD exchange rates, where even low-cost Apple smartphones are beyond the financial capabilities of the majority of users.
Not only that, the populations of India and China account for about 1/3 of the world's population, so the popularity of the Android operating system in these countries has put iOS at a big disadvantage. That is why Apple is currently promoting its business plans in these populous world markets.
3. Android devices can connect to many devices
Although Apple has opened up the IOS ecosystem to include several third-party devices, it is still a relatively closed mobile platform. However, Android has a much broader ecosystem of peripherals and wearables. This means you can have a Samsung smartwatch, a Google Home speaker, and a Huawei smartphone, and the different devices will work together.
Furthermore, data transfer and device synchronization are much simpler. This broader ecosystem attracts users who don't want to be tied to certain hardware brands. After all, if you change the Android device you use, this doesn't make all your peripherals incompatible. You can also keep many similar cables and accessories.
4. Android is becoming more and more practical

In recent years, Android has caught up to IOS in many aspects, with Google Assistant and its excellent voice control features achieving great success. Many apps that were previously iOS-only have now launched Android versions, and Google has also introduced AI to help automate your smart home. Official Google services and major app developers have significantly raised the overall quality of Android software.
Furthermore, Android integrates many expected features with each new version and improves the entire product. Now, Android phone manufacturers have paid more attention to optimizing the Android platform so that users can use the device more optimally and practically, instead of just racing for configuration like before.
5. Ability to customize and install APK files
If you are too bored with the current features and interface on your Android device You can try to customize it by installing ROMs of other platforms, something that is very difficult to do on iOS.
Due to the open-source nature of the Android operating system, anyone can obtain its source code. This also means that manufacturers, as well as independent programmers, can freely customize Android to get the best performance or remove unnecessary features.
Currently, in the Android user community, there are many ROMs with high customization, most notably EvolutionX or lineage OS, in addition to other ROMs that Make your phone simpler and optimize performance like Pixel Experience or CyanogenMod. Android group pages also have a large number of members They can help with any problems you encounter during ROM installation or use.
Besides great customization capabilities, the ability to install APK files is also an advantage for Android users to continue using old devices. Most of you will often download applications on your phone through app stores like CH Play or APPSTORE. But sometimes there are some apps you won't find on these stores for various reasons.
At this time, the ability to install APK files on Android will shine. You can also install and experience new Android builds that are often leaked in advance to use exciting new features, or download applications that are limited to certain regions so cannot be downloaded directly from the app store.
In addition, installing APK files also helps you update new application versions faster or you can even install older versions of the application to optimize for your old devices. Besides, if your device does not have access to the Play Store app store, installing the APK file will be your only choice.
In short, the diversity of Android as well as the competition between operating systems promotes a technology race between brands, helping users easily find a device that suits their financial capabilities and meets their needs meet your own needs.
[reference resources]
- https://fptshop.com.vn/tin-tuc/danh-gia
- https://www.thegioididong.com/tin-tuc/dien-thoai-thong-minh-da-thay-doi-cuoc-song-cua-chung-ta-1404983
- https://medium.com/android-news/the-best-android-sdk-tools-of-the-year-b546f66edf28
- https://support.google.com/android/answer/12761388?hl=en