Following the post "Overview of DICOM Image", this time I’ll introduce DICOM Services, which are used to store and share medical images between different systems.
What is a DICOM Service?
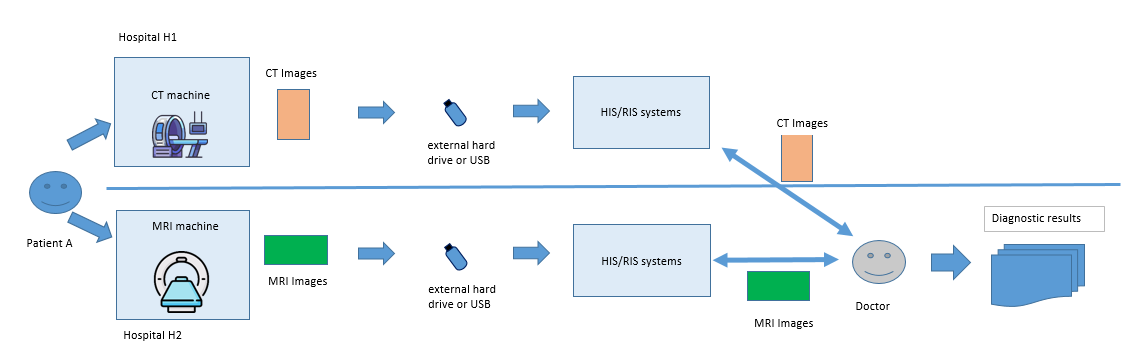
First, let’s look at the following scenario without DICOM services
- In the first time, Patient A goes for a CT scan at Hospital H1. After the scan, the technician exports the DICOM images from the CT machine to an external hard drive or USB, then manually transfers it to another device at Hospital H1 to import the data into the HIS/RIS system of H1.
- In the second time, Patient A goes for an MRI scan at Hospital H2. The technician exports the DICOM images from the MRI machine to an external hard drive or USB and manually transfers it to another device at Hospital H2 to import the data into the HIS/RIS system of H2.
- Now, if a doctor at Hospital H2 wants to review the images taken at Hospital H1 for a combined diagnosis, they need to access Hospital H1’s HIS/RIS system, search for Patient A’s information, and download the DICOM images to their PC. Next, the doctor accesses Hospital H2’s HIS/RIS system and imports the data from H1 to use.
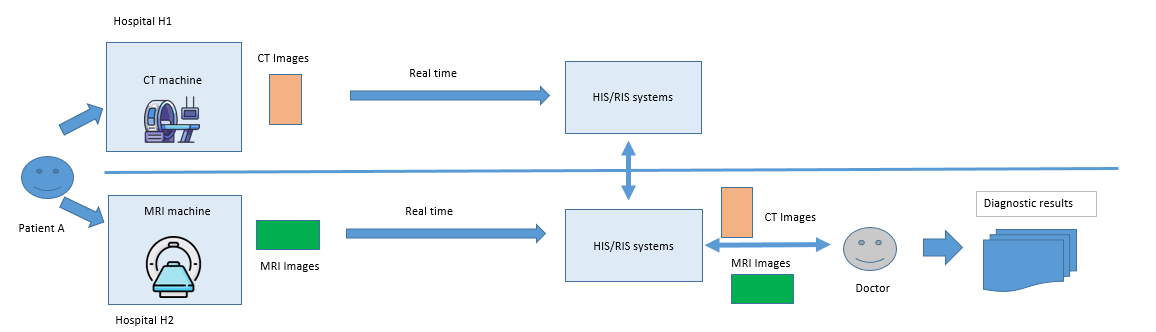
With DICOM Services
- In the first time, Patient A goes for a CT scan at Hospital H1. Using the DICOM Storage Service, the CT images are automatically sent to the HIS/RIS system immediately. A specialist can access and view the images on HIS/RIS system almost instantly.
- In the second time, Patient A goes for an MRI scan at Hospital H2. Using the DICOM Storage Service, the MRI images are automatically sent to the HIS/RIS system. A specialist can access and view the images on HIS/RIS system almost instantly.
- If a doctor at Hospital H2 wants to review the images taken at Hospital H1 for a combined diagnosis, they only need to enter the search information into Hospital H2’s HIS/RIS system. The HIS/RIS system at H1, connected to the HIS/RIS system at H2, will automatically search for and retrieve the images quickly.
Through this example, we can see some of the benefits that DICOM Services provide.
Below are the main DICOM Services
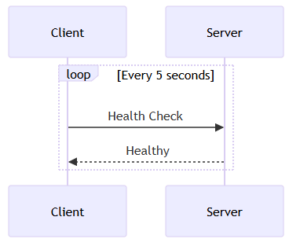
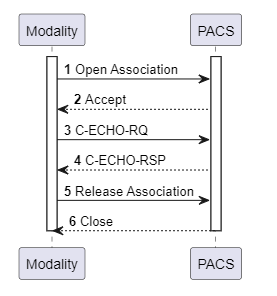
DICOM Verification Service
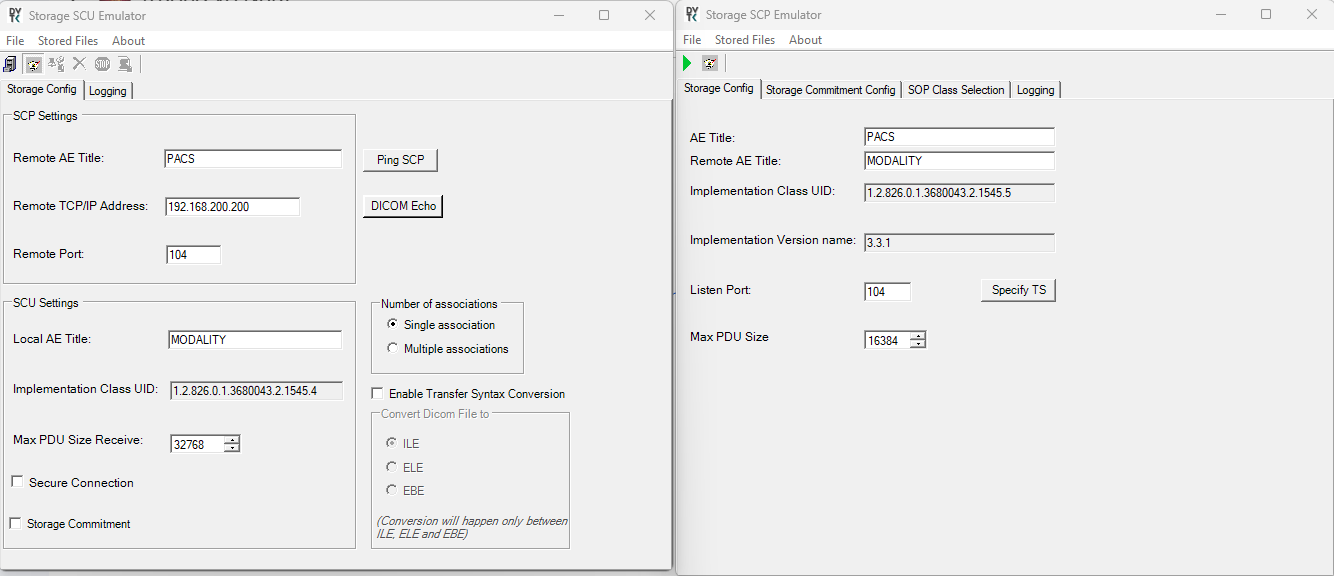
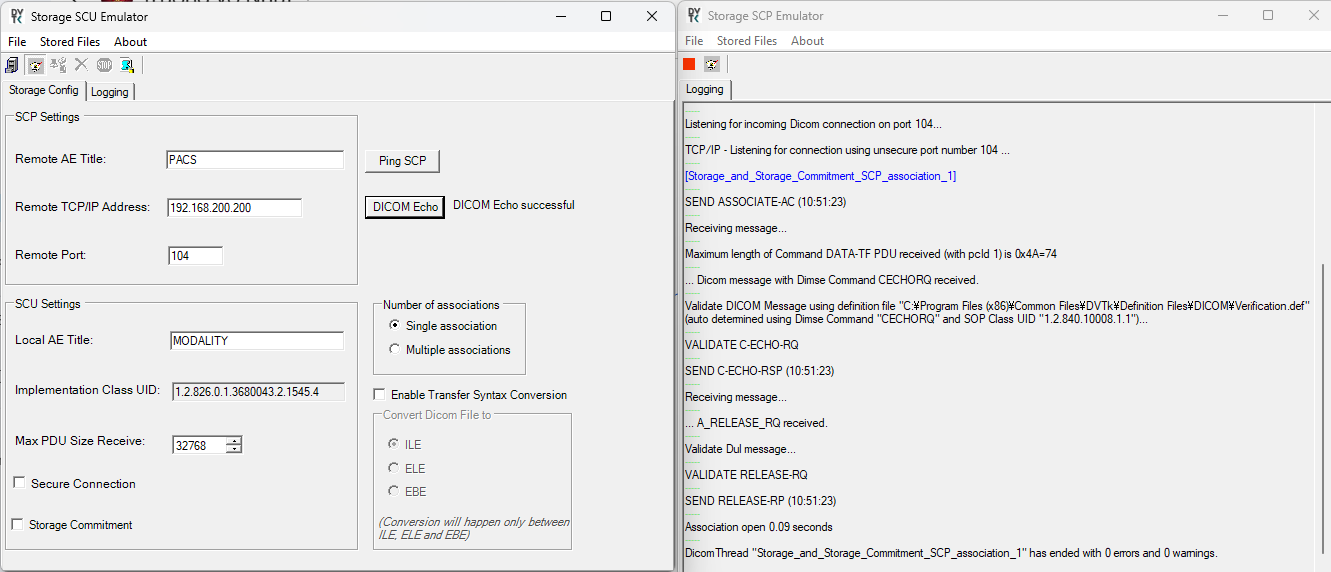
This service is used to test the connectivity between medical devices or systems before starting official data transfer tasks. A C-ECHO-RQ message is sent from a client device to the target device over TCP/IP. The target device responds with a C-ECHO-RSP message. If the C-ECHO-RSP message indicates success, it means the devices are ready to communicate with each other.
Storage Service
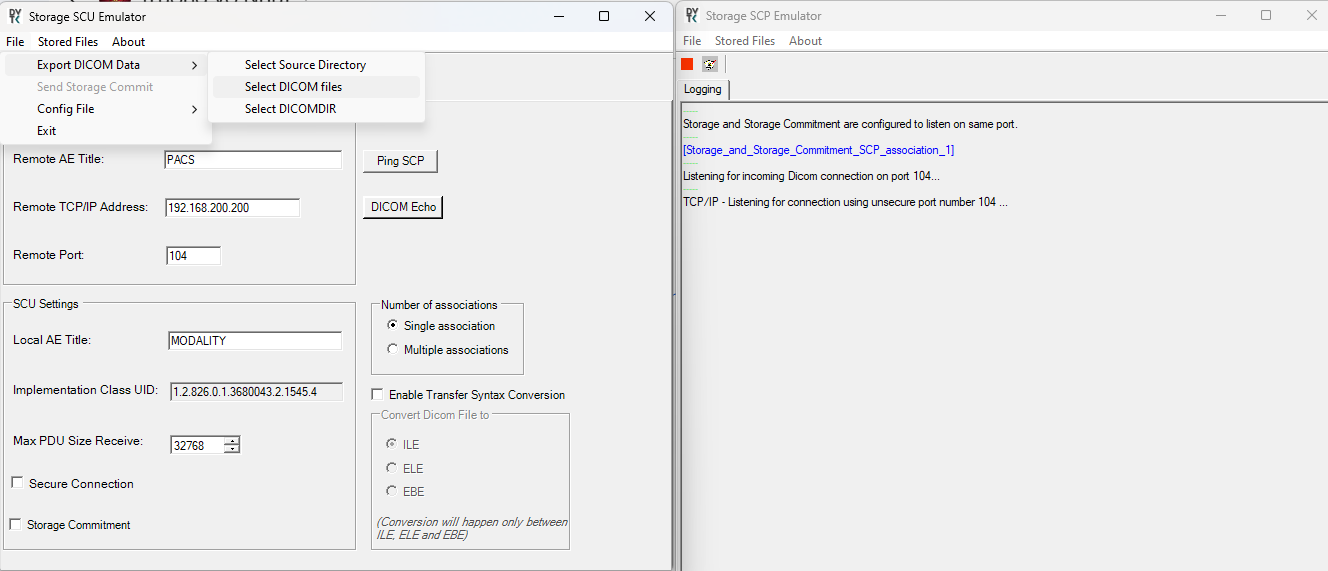
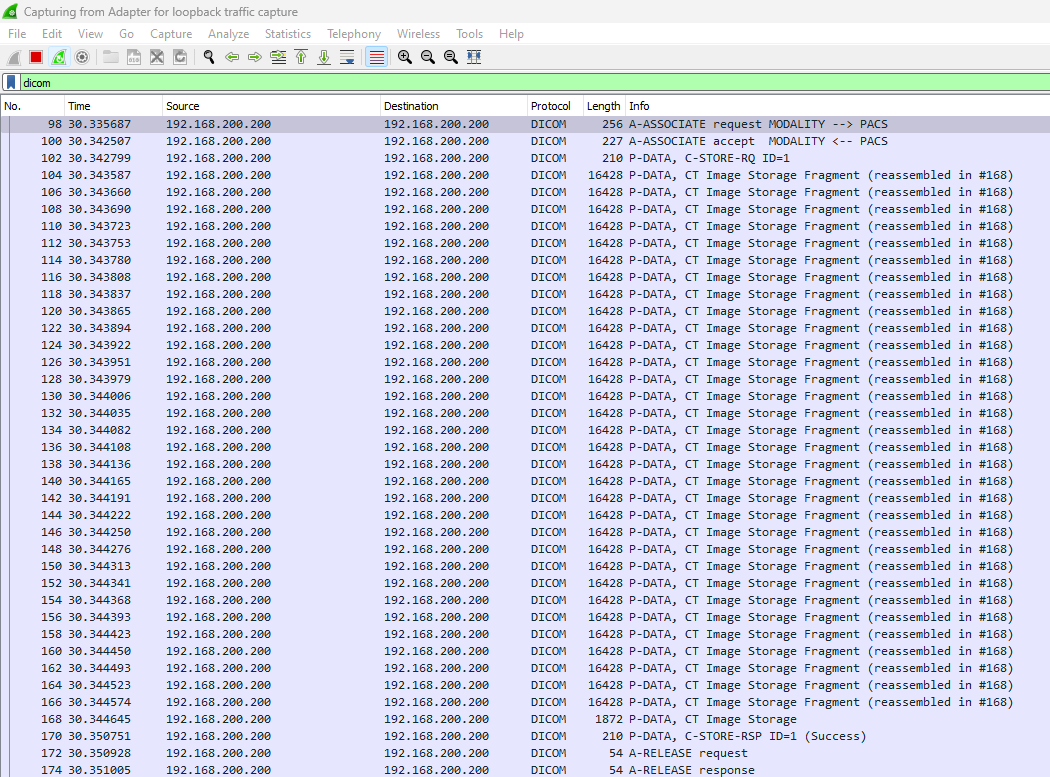
Used to store DICOM files or a series of DICOM files from the client to the target device. A C-STORE-RQ message with data is sent from the client to the target device over TCP/IP. Once the data is successfully received, the target sends a C-STORE-RSP message with a success status back to the client.
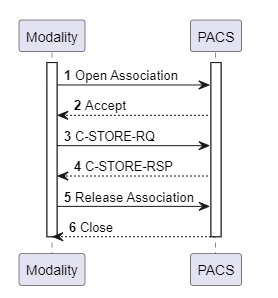
Storage Commitment Service
This service is an extension of the Storage Service. For the Storage Service, the success message received by the client only confirms that the data was received by the target, not that it was securely stored. Storage Commitment Service, however, ensures that the data sent by the client is securely stored by the target and can be used later.
For example, after an MRI scan, the MRI images sent to the PACS device can be safely deleted from the MRI device once a commitment from PACS confirms safe storage. The client sends an N-ACTION-RQ message, and the target responds with N-ACTION-RSP, then sends an additional N-EVENT-REPORT message to the client confirming secure storage. Finally, the client sends an N-EVENT-REPORT-RSP message to acknowledge the commitment from the target.

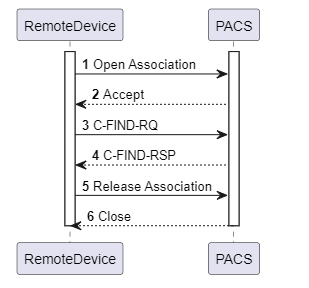
Query/Retrieve Service
When a client wants to search for information on the target device, it sends a C-FIND-RQ message with search conditions. The search results are returned from the target via a C-FIND-RSP message.
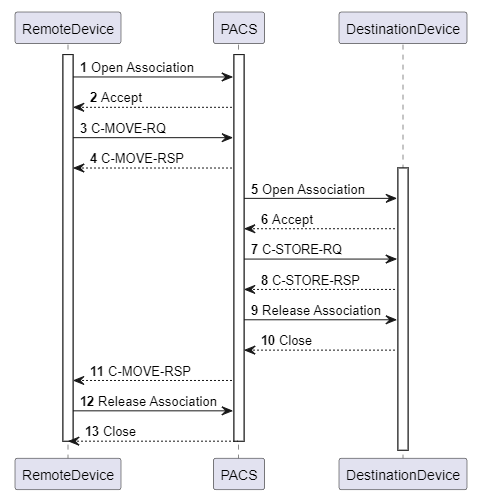
If the client wants to request the target to send data to another location, it sends a C-MOVE-RQ message specifying the items to be retrieved. Using DICOM Storage Service, the target then transfers the data to the location designated by the client. The results of this transfer are returned via a C-MOVE-RSP message.
Modality Worklist Service
Modality devices (such as X-ray, CT, MRI, etc.) connect to information systems like HIS/RIS, then use this service to retrieve a list of patients needing imaging. This includes details like the patient's name, patient ID, exam type, and scheduled time, helping to reduce manual entry and improve the accuracy of linking images with patient information.
The modality also sends a C-FIND-RQ message to the HIS/RIS system, as mentioned in the Query/Retrieve Service section above. However, when requesting a worklist, the content within the C-FIND-RQ message will specify that the target object to retrieve is the worklist, identified by the SOP Class UID "1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.31". HIS/RIS responds with a worklist containing the necessary information for each patient and exam via a C-FIND-RSP message.
For more details about SOP Class UID regulations, please refer to the following link:
https://dicom.nema.org/medical/dicom/current/output/chtml/part04/sect_b.5.html

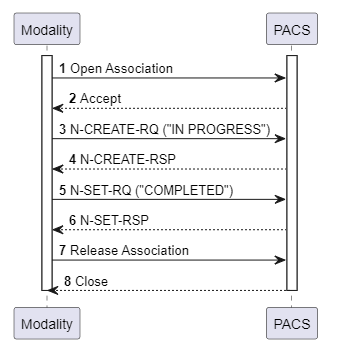
Modality Performed Procedure Step (MPPS) Service
Modality devices connect to systems like HIS/RIS and use this service to send information about the steps and status of the imaging procedure to HIS/RIS systems. This ensures the imaging procedure is continuously and accurately updated, from start to finish.
When imaging begins, the modality sends a N-CREATE-RQ message with "IN PROGRESS" to the HIS/RIS. If the procedure is interrupted, the modality sends a N-SET-RQ message with "DISCONTINUED" When the imaging is completed, the modality sends a N-SET-RSP message with "COMPLETED" including final details like the number of images, duration, and other information to document the procedure. The HIS/RIS system also responds with corresponding N-CREATE-RSP and N-SET-RSP messages.
To better understand the operation of DICOM services, you can use common simulation tools like DVTK and DCMTK.
Below is an example demonstrating how to use a DICOM service with the DVTK emulator and observe the results using Wireshark.
DICOM Verification Service

Storage Service
These are brief overviews of the main DICOM services widely used in healthcare systems today. Based on this information, I hope you find it easier to read and understand related documents and specifications.
The above is an overview of the main DICOM services currently widely used in healthcare systems. Based on this information, I hope it’s easier for you to read and understand related documentation and specifications.
For more details, please refer to the official DICOM standard website:
https://dicom.nema.org/medical/dicom/current/output/chtml/part07/chapter_9.html
Building next-generation healthcare imaging solutions?
Partner with us to deliver cloud-ready, standards-compliant DICOM services tailored to your product.
Contact IVC for a Free ConsultationReferences
https://dicom.offis.de/en/general/dicom-introduction/
https://www.neologica.it/eng/Tutorial/DICOMServices
External image links
https://www.flaticon.com/free-icons/ct-scan
https://www.flaticon.com/free-icons/mri
https://www.flaticon.com/free-icons/radiology
Featured image designed by Freepik