Event handling is a critical aspect of modern programming, especially in interactive applications such as GUI software, games, and real-time systems. While C++ lacks built-in event-handling mechanisms, its flexibility allows developers to design efficient systems or leverage powerful libraries like Qt and wxWidgets.
This guide will take you through the essentials of event handling in C++, covering fundamental concepts and practical implementations.
1. What is Event Handling?
Event handling involves responding to actions or events within a program. Examples of events include:
- A user clicking a button.
- Moving the mouse or entering keyboard input.
- A signal triggered within the program.
Unlike some other programming languages with built-in support for event handling, C++ requires developers to design their own systems or utilize external libraries.
2. Key Components of an Event-Handling System
2.1. Event
An event represents an action or signal triggered by a user or the system, such as:
- A mouse click (
MouseClickEvent). - A key press (
KeyPressEvent).
2.2. Event Listener
An event listener monitors and detects specific events, taking appropriate actions when they occur.
2.3. Event Handler
An event handler is the function or code block executed in response to an event.
3. Building a Basic Event-Handling System in C++
3.1. Using Callback Functions
Callback functions are one of the simplest methods for handling events in C++.
Example:
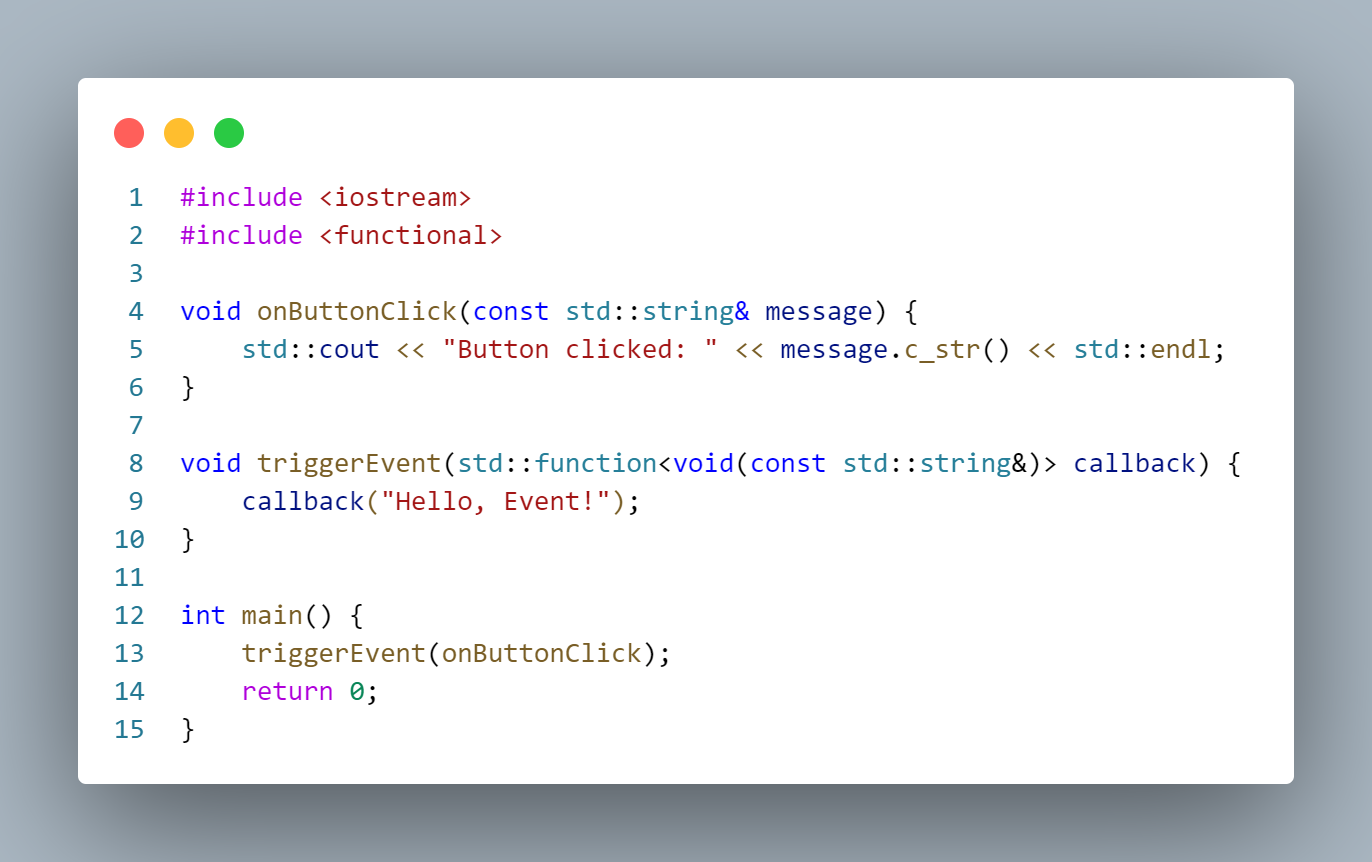
Explanation:
onButtonClickis the event handler function.triggerEventinvokes the callback function when the event occurs.
3.2. Implementing the Observer Pattern
The Observer Pattern is a design pattern where one object (Observer) reacts to changes or events from another object (Subject).
Example:
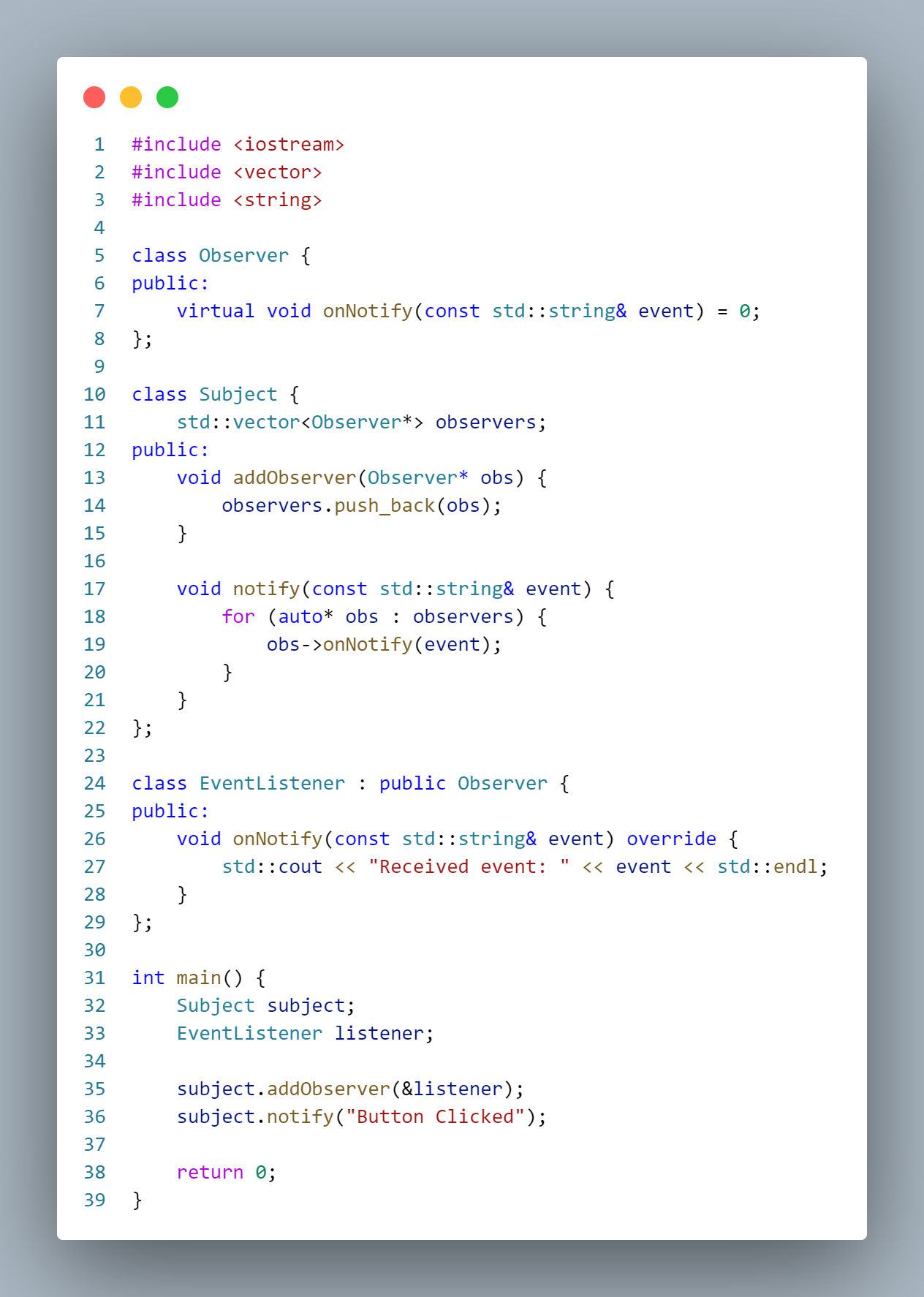
Explanation:
- Observer: An interface for defining objects that listen for events.
- Subject: Manages a list of observers and notifies them when an event occurs.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Event Handling in C++
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Customizable event-handling systems tailored to specific needs.
- Performance: Well-designed systems can achieve high efficiency.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Building systems from scratch can be challenging.
- No Built-in Support: Relies on external libraries or design patterns.
5. Real-World Applications
5.1. Game Development
Game engines like Unreal Engine (built with C++) use event-driven models to handle user inputs and game logic.
5.2. GUI Programming
Libraries such as Qt, wxWidgets, and FLTK enable developers to create responsive graphical applications with event handling.
6. Conclusion
Event handling is a foundational concept in programming, enabling applications to react dynamically to user or system actions. While C++ lacks native support, you can utilize strategies like callback functions, the Observer Pattern, or libraries like Qt to implement robust systems.