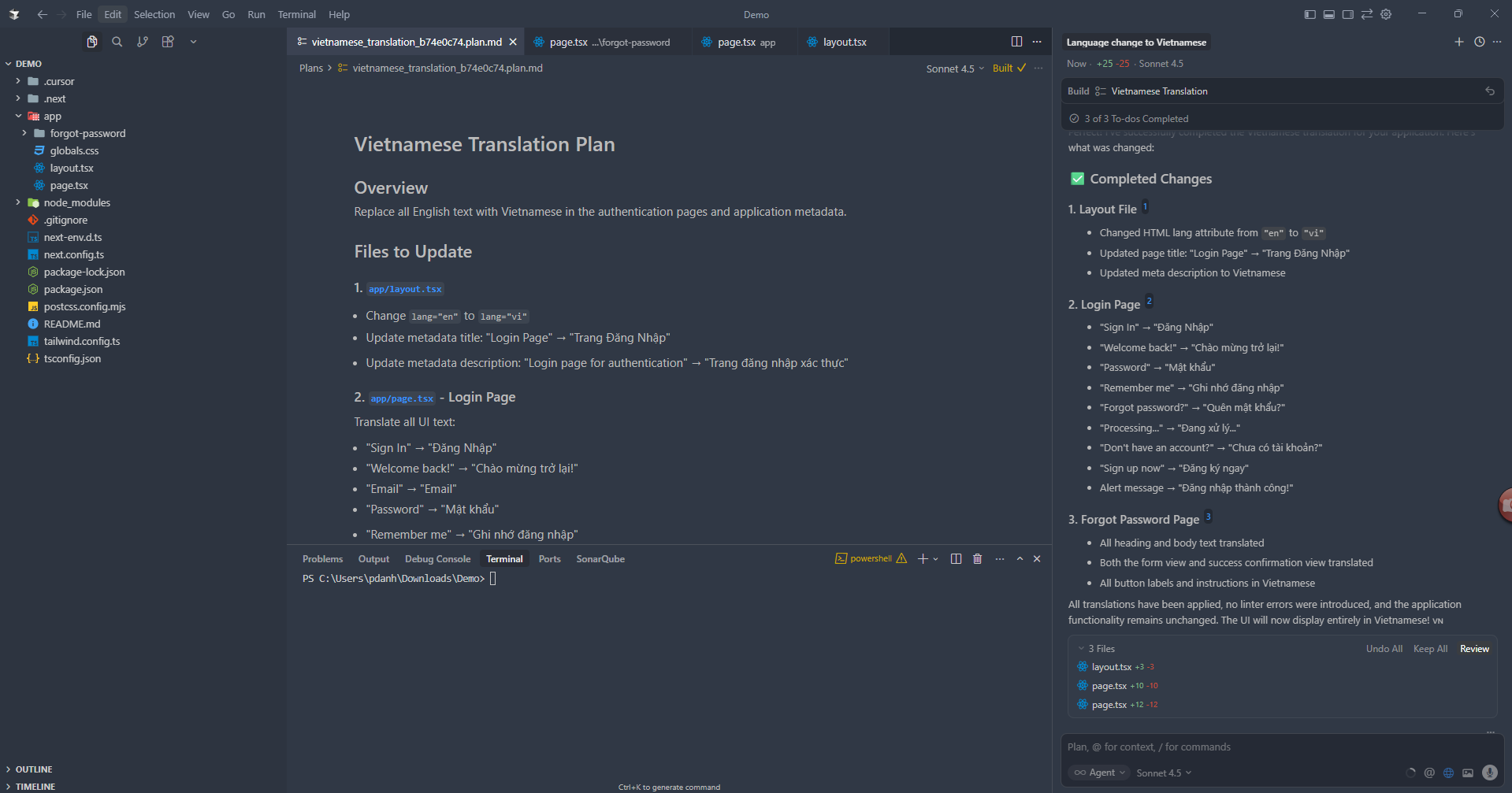
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a crucial security feature that adds an extra layer of protection to your web applications. In this tutorial, we'll learn how to implement Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) authentication in a Flask application, similar to what you see in Google Authenticator.
What is TOTP?
TOTP (Time-based One-Time Password) is a widely used algorithm that generates temporary passwords based on:
- A shared secret key
- The current time
The generated passwords typically:
- Are 6 digits long
- Valid for 30 seconds
- Compatible with apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, etc.
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, you'll need:
- Python 3.x
- Flask
- Additional Python packages:
flask-login flask-sqlalchemy pyotp qrcode Pillow
Project Structure
your-project/
├── app.py # Main application file
├── extensions.py # Flask extensions
├── models.py # Database models
└── templates/ # HTML templates
├── index.html
├── register.html
├── login.html
├── setup_2fa.html
├── verify_2fa.html
└── dashboard.htmlImplementation Steps
1. Setting up the Database Model
First, we create a User model that stores the TOTP secret alongside other user information:
class User(UserMixin, db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
username = db.Column(db.String(80), unique=True, nullable=False)
password_hash = db.Column(db.String(120), nullable=False)
totp_secret = db.Column(db.String(32), nullable=False)
2. User Registration with 2FA Setup
During registration:
- Generate a unique TOTP secret for each user
- Create a QR code containing the TOTP configuration
- Display the QR code to the user for scanning
@app.route('/register', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def register():
if request.method == 'POST':
# Generate TOTP secret
totp_secret = pyotp.random_base32()
# Create user
user = User(username=username, totp_secret=totp_secret)
user.set_password(password)
# Generate QR code for TOTP setup
totp = pyotp.totp.TOTP(totp_secret)
provisioning_uri = totp.provisioning_uri(
username,
issuer_name="Your App Name"
)
3. Two-Step Login Process
The login process is split into two steps:
- Username/Password Verification
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if user and user.check_password(password):
session['username'] = username
return redirect(url_for('verify_2fa'))
- TOTP Code Verification
@app.route('/verify-2fa', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def verify_2fa():
if request.method == 'POST':
totp = pyotp.TOTP(user.totp_secret)
if totp.verify(totp_code, valid_window=1):
login_user(user)
return redirect(url_for('dashboard'))
Security Considerations
-
Time Synchronization: TOTP relies on synchronized time between the server and client. Use
valid_windowparameter to allow for slight time differences. -
Secret Key Storage: Always store TOTP secrets securely in your database. They are as sensitive as passwords.
-
Backup Codes: Consider implementing backup codes for users who lose access to their authenticator app.
-
QR Code Security: Only show the QR code once during setup and require re-authentication to view it again.
User Experience Tips
-
Clear Instructions: Provide clear instructions for users to set up their authenticator app.
-
Fallback Options: Display the TOTP secret key as text for users who can't scan the QR code.
-
Error Messages: Provide helpful error messages when verification fails.
Testing
Test your 2FA implementation thoroughly:
- Registration flow
- QR code scanning
- Time synchronization issues
- Invalid code attempts
- Session handling
- Logout functionality
Conclusion
Implementing 2FA using TOTP in Flask is straightforward with the right libraries. This implementation provides a solid foundation for securing your web application with two-factor authentication. Remember to adapt the security measures based on your specific requirements and always follow security best practices.
The complete source code demonstrates a working implementation that you can use as a starting point for your own projects.
Further Improvements
Consider adding these features to enhance your 2FA implementation:
- Backup codes generation
- Remember trusted devices
- 2FA recovery process
- Rate limiting for failed attempts
- Audit logging for security events
Remember that security is an ongoing process, and it's important to keep your dependencies updated and regularly review your security measures.
Whether you need scalable software solutions, expert IT outsourcing, or a long-term development partner, ISB Vietnam is here to deliver. Let’s build something great together—reach out to us today. Or click here to explore more ISB Vietnam's case studies.
References
[1]. Internet Engineering Task Force. (2011, May). RFC 6238: TOTP - Time-Based One-Time Password Algorithm. Retrieved from https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6238
[2]. SQLAlchemy. (2023). Flask-SQLAlchemy Documentation. Retrieved from https://flask-sqlalchemy.palletsprojects.com/
[3]. OWASP Foundation. (2023). Multi-Factor Authentication Cheat Sheet. Retrieved from https://cheatsheetseries.owasp.org/cheatsheets/Multifactor_Authentication_Cheat_Sheet.html
[4]. NIST. (2017, June). Special Publication 800-63B: Authentication and Lifecycle Management. Retrieved from https://pages.nist.gov/800-63-3/sp800-63b.html