In modern web applications, performance and user experience are very important. Users always expect immediate responses to every action. However, some tasks such as sending emails, processing images or generating reports take a long time. If we perform them right in the process of responding to requests, the application will become slow.
The Queue is the solution to solve this problem. In this article, we will know what Laravel Queues is, why we should use it, and the simplest way to implement it.
What is Queue?
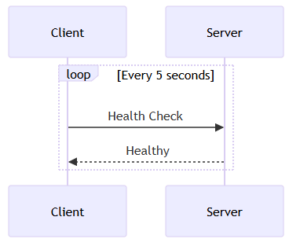
Queues allow us to push time-consuming tasks to the background, instead of executing them immediately when a user sends a request.
Some examples of using Queues:
-
- Sending an email.
- Processing and resizing images when users upload.
- Sending notifications to multiple people.
- Generating PDF reports.
- Processing payments.
Why should we use Queues?
For example, when a user registers for an account, we want to send a welcome email.
Without Queues:
-
- Save user information.
- Create email content.
- Send an email.
- Return results to the browser.
If sending an email takes 3-5 seconds, users will have to wait a long time.
Using Queues:
-
- Save user information.
- Push the email request to the queue.
- Return results immediately to the user.
- Send an email in the background.
Here is much more effective!
How to implement Laravel Queues simply
Step 1: Configure Queues Driver
Laravel supports many types, such as database, Redis, Amazon SQS, etc
Here we use the database driver for the example.
In the .env file, edit the following line:
QUEUE_CONNECTION=database
Create the database table to hold the jobs by running the migration:
php artisan queue:table
php artisan migrate
Step 2: Create a Job
Run the command:
php artisan make:job SendWelcomeEmail
This will generate a class in app/Jobs/SendWelcomeEmail.php
In the file app/Jobs/SendWelcomeEmail.php, we add the email sending logic:
public function handle()
{
Mail::to($this->user->email)->send(new WelcomeEmail($this->user));
}
Step 3: Dispatching Jobs
In Controller, when the user registers, we use the dispatch on the job itself. The arguments passed to the method will be set to the job's constructor
SendWelcomeEmail::dispatch($user);
At this time, the email sending job has been queued.
Step 4: Run the Queue Worker
To start a queue worker and process jobs, we need to run the command below
php artisan queue:work
Worker is a long-lived process, so during deployment, it will not automatically recognize and adapt to changes in source code, so we need to restart it during deployment, with the command:
php artisan queue:restart
To keep the queue process running permanently in the background, we need to use a process monitor such as
Supervisor in production to keep workers running.
Conclusion
The Queue is a powerful tool that helps us improve application performance and provide a smooth user experience. Time-consuming tasks such as sending emails, processing images, generating reports, etc., should be queued to run in the background.
If you are building a Laravel application and have not yet used Queue, you should try to implement it in your application. This will not only make your application run faster but also make it easier to extend and manage later.
Whether you need scalable software solutions, expert IT outsourcing, or a long-term development partner, ISB Vietnam is here to deliver. Let’s build something great together—reach out to us today. Or click here to explore more ISB Vietnam's case studies.
[References]
- https://laravel.com/docs/12.x/queues
- https://viblo.asia/p/gioi-thieu-ve-queues-trong-laravel-gAm5yqgD5db
- https://www.luckymedia.dev/blog/laravel-for-beginners-using-queues (Image source)