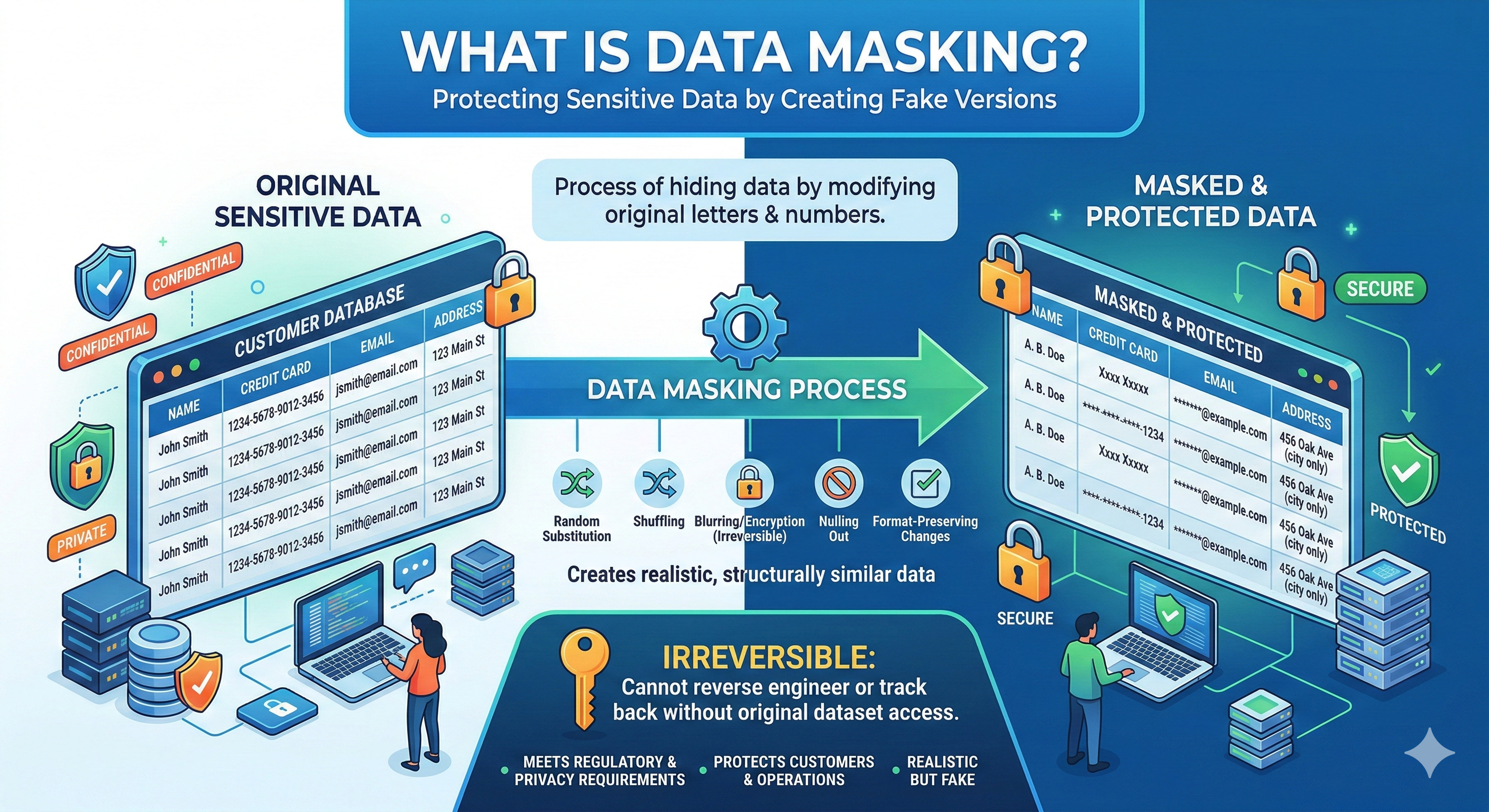
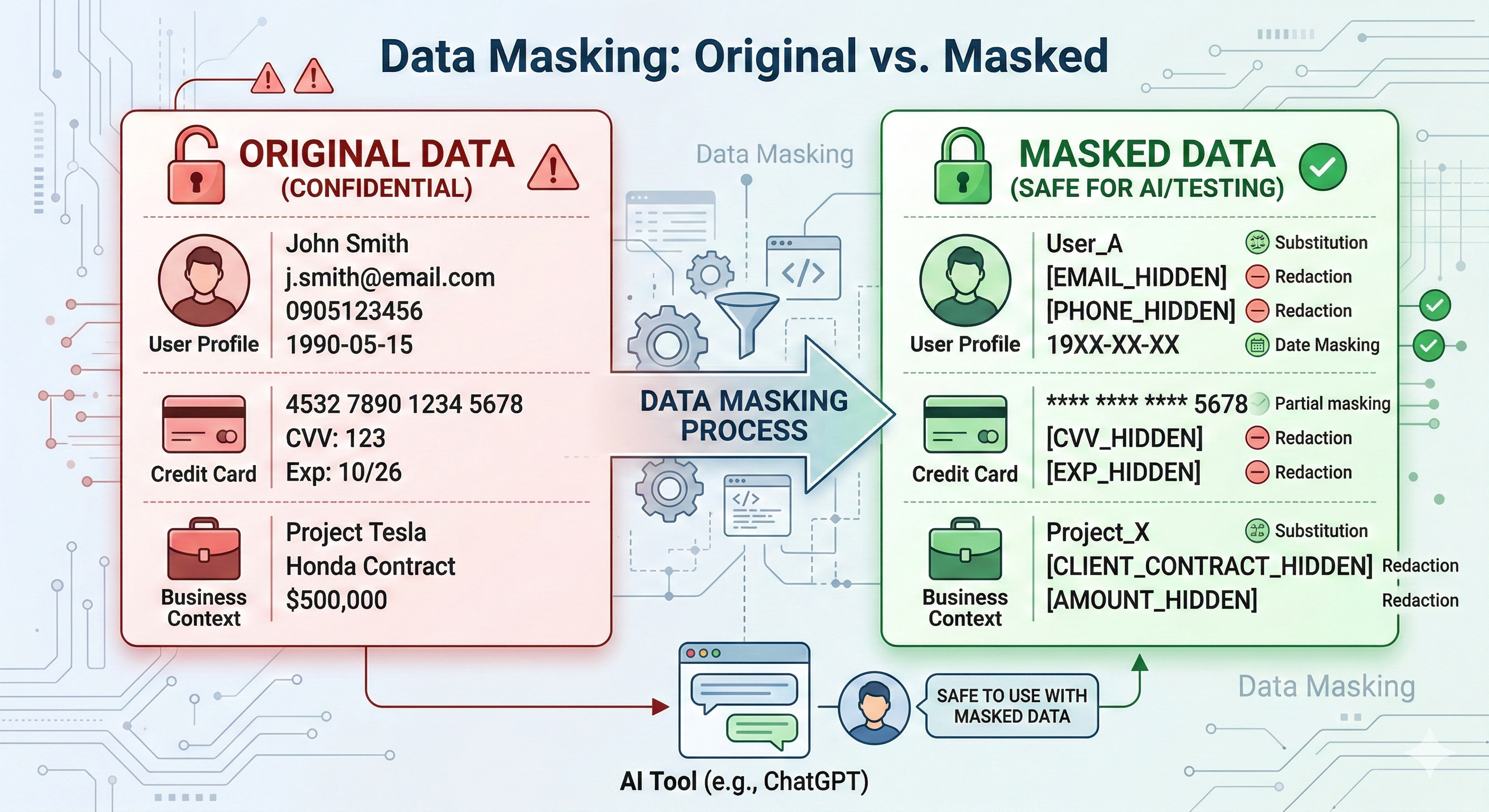
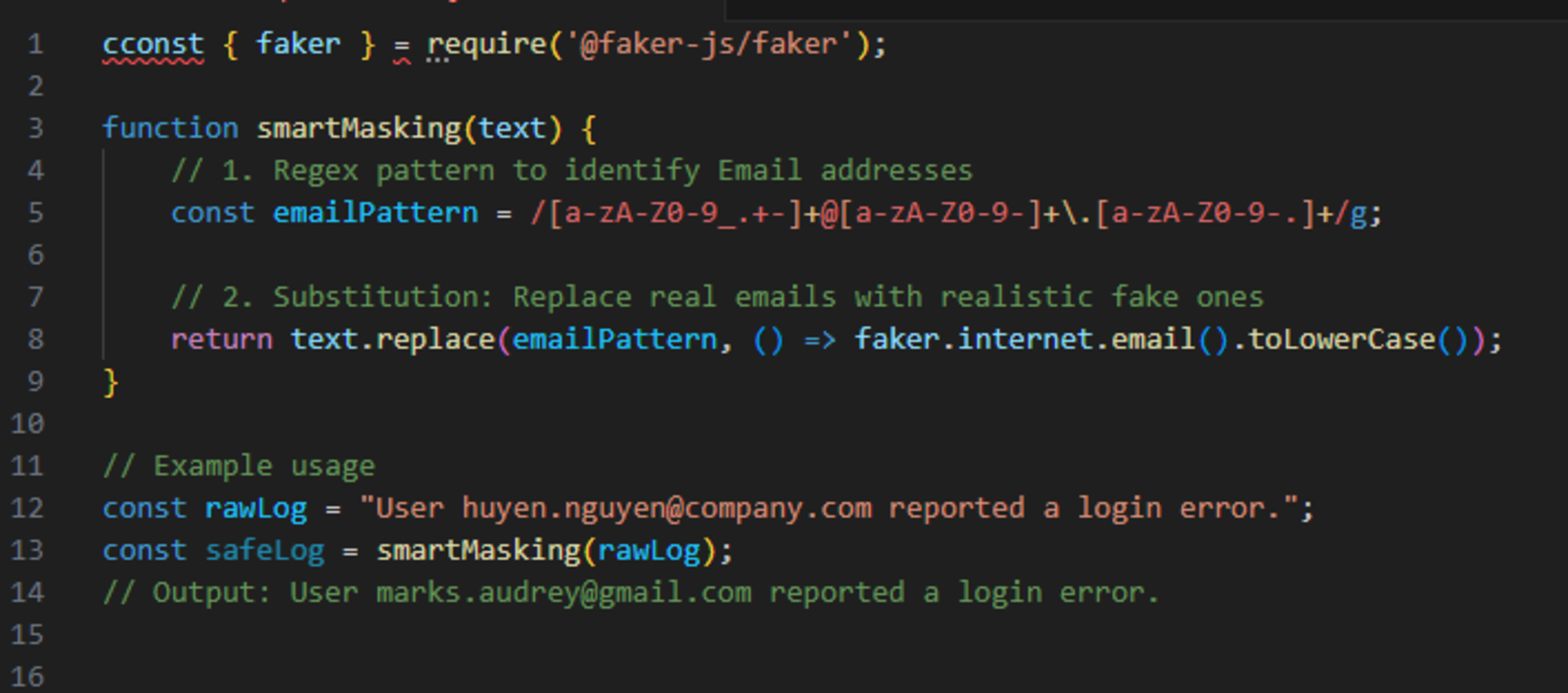
Master the foundational benefits of AWS Cloud. Learn why organizations worldwide choose AWS and how cloud infrastructure transforms business operations.
Welcome back to our AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02) exam series! In the first post, we explored the complete exam outline and structure. Today, we're diving into the first part of Domain 1: Cloud Concepts - the foundational domain that represents 24% of your exam score.
Think of Domain 1 as the "why" of cloud computing. Before you learn about specific AWS services (which we'll cover in later posts), you need to understand why organizations move to the cloud and what principles guide good cloud architecture. This domain ensures you can articulate the value proposition of AWS to stakeholders, whether they're technical or business-focused.
Domain 1 consists of four task statements. We'll cover these across multiple posts. In this post (Part 1), we'll focus on Task Statement 1.1: The Benefits of AWS Cloud - understanding what makes AWS attractive to organizations.
Domain 1 Overview: What You Need to Know
Domain 1 focuses entirely on concepts rather than technical implementation. You won't be asked to configure services or write code. Instead, you'll need to demonstrate understanding of:
- Why businesses choose AWS - The tangible benefits (This post - Part 1)
- How to design well - Best practice principles (Part 2)
- How to migrate effectively - Strategies and frameworks (Part 3)
- How cloud saves money - Economic advantages (Part 3)
Let's start with understanding the core benefits that make AWS attractive to organizations worldwide.
Task Statement 1.1: Define the Benefits of the AWS Cloud
This task statement focuses on understanding what makes AWS Cloud valuable compared to traditional IT infrastructure.
Global Infrastructure Benefits
Speed of Deployment: In traditional data centers, purchasing and setting up new servers could take weeks or months. With AWS, you can provision resources in minutes. For example, if your marketing team suddenly needs a new web application for a campaign launching next week, you can deploy it on AWS EC2 instances within hours, not months.
Global Reach: AWS operates in multiple geographic regions worldwide, each containing multiple Availability Zones (separate data centers). This means:
- A company based in the US can easily serve customers in Europe, Asia, or South America with low latency
- You can deploy applications close to your users without building physical data centers
- Content can be cached at edge locations (over 400 globally) for faster delivery
Real-World Example: A streaming service wants to expand from the US to Japan. Instead of building data centers in Tokyo (costing millions and taking years), they can deploy their application to AWS's Tokyo Region in days, instantly providing low-latency service to Japanese users.
High Availability
High availability means your applications stay running even when something fails. AWS achieves this through:
- Multiple Availability Zones: Each AWS Region has at least 3 separate data centers (AZs) with independent power, cooling, and networking
- Fault isolation: If one AZ experiences issues, your application continues running in other AZs
- Built-in redundancy: Many AWS services automatically replicate data across multiple locations
Example: An e-commerce site runs on EC2 instances in 3 different Availability Zones. During a power outage in one AZ, customers continue shopping without interruption because the other 2 AZs handle all traffic seamlessly.
Elasticity
Elasticity is the ability to automatically scale resources up or down based on demand. This is one of cloud's most powerful benefits.
- Scale up: During peak times, automatically add more servers
- Scale down: During quiet periods, reduce servers to save costs
- No manual intervention: AWS Auto Scaling handles this automatically
Real-World Scenario: A tax preparation website sees massive traffic increases in March and April but minimal traffic the rest of the year. With AWS elasticity:
- In tax season: Automatically scales to 100 servers to handle 1 million daily users
- In summer: Scales down to 5 servers for the 10,000 daily users
- Result: Only pay for what you need, when you need it
Agility
Agility in cloud means the ability to quickly experiment, innovate, and respond to market changes without large upfront investments.
- Faster time to market: Launch new products in days instead of months
- Lower risk of experimentation: Try new ideas with minimal cost; shut them down if they don't work
- Focus on innovation: Spend time building features, not managing infrastructure
Example: A startup wants to test if their new AI-powered app will attract users. On AWS, they can:
- Deploy a prototype in 2 days
- Run it for a month at $100 cost
- If it fails, delete everything with no long-term commitment
- If it succeeds, scale up immediately
Compare this to traditional IT: purchasing servers ($50,000+), setting them up (3 months), then being stuck with hardware even if the project fails.
Key Takeaways
Understanding AWS Cloud benefits is essential for the CLF-C02 exam. Remember these core advantages:
- Speed: Deploy resources in minutes, not months
- Global Reach: Serve users worldwide without building physical infrastructure
- High Availability: Keep applications running even when failures occur
- Elasticity: Automatically scale resources to match demand
- Agility: Experiment quickly and innovate without large upfront costs
What's Next?
Now that you understand why organizations choose AWS, the next step is learning how to design cloud systems well.
In Part 2, we'll explore:
- The AWS Well-Architected Framework – Six pillars of cloud design excellence
- Design principles for each pillar with practical examples
- How to distinguish between pillars in CLF-C02 exam questions
- Practice questions to reinforce your understanding
These design principles are essential not only for passing the CLF-C02 exam, but also for building reliable, secure, and cost-effective cloud solutions in real-world scenarios.
Which AWS Cloud benefit do you find most valuable in your work? Have you experienced any of these benefits firsthand? Share your experience in the comments below!
Whether you need scalable software solutions, expert IT outsourcing, or a long-term development partner, ISB Vietnam is here to deliver. Let’s build something great together—reach out to us today. Or click here to explore more ISB Vietnam's case studies.
References
[1]. AWS Global Infrastructure. Retrieved from https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/
[2]. AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide (CLF-C02). Retrieved from https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-cloud-practitioner/