In the era of modern web applications, security is one of the most critical factors, especially when handling and storing sensitive data. Next.js - a powerful framework based on React - not only optimizes performance but also provides enhanced security features through Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and API Routes.
This article will help you understand how to use Next.js to safeguard data and minimize security risks.
Security Risks When Fetching API Directly
Most applications built with client-side rendering (CSR) make API requests directly from the browser using libraries like fetch or axios. However, this approach poses several risks:
- Exposure of sensitive information: Details like tokens, API endpoints, or processing logic can be exposed on the client.
- Vulnerability to XSS (Cross-Site Scripting): Hackers can inject malicious scripts into the interface to steal data or hijack user sessions.
- Lack of encryption: Unprotected data can be intercepted during transmission.

Next.js: A Comprehensive Security Solution
1. Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
SSR processes data and renders HTML on the server before sending it to the client, providing better protection for sensitive data.
Security Benefits of SSR:
- Hides data from the client: Sensitive information like API keys or user details is handled only on the server.
- Mitigates XSS risks: Hackers find it harder to inject malicious scripts.
- Access control: Client requests are authenticated on the server before any actions are performed.
SSR Configuration Example:
export async function getServerSideProps(context) { const res = await fetch("https://api.example.com/data", { headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.API_KEY}` }, }); const data = await res.json(); return { props: { data } };}2. API Routes
Next.js supports API Routes, allowing you to build API endpoints directly within the project without a separate backend.
Benefits of API Routes:
- Server-only endpoints: Cannot be accessed directly from the client.
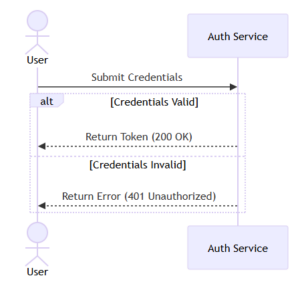
- Built-in authentication: Easily implement security methods like JWT or OAuth.
API Route Configuration Example:
export default async function handler(req, res) { if (req.method === "POST") { const { token } = req.body; if (token !== process.env.SECRET_TOKEN) { return res.status(401).json({ error: "Unauthorized" }); } res.status(200).json({ message: "Success" }); } else { res.status(405).json({ error: "Method Not Allowed" }); }}3. Combining SSR and API Routes

Workflow:
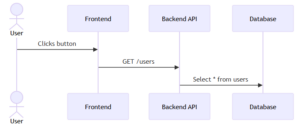
- Users send requests from the Next.js UI.
- The Next.js server (SSR or API Route) processes logic, authenticates data, and forwards requests to the backend API (if needed).
- The backend API interacts with the database, processes requests, and returns data to the server.
- The server sends processed data back to the user interface.
4. Key Security Features
-
Authentication and Authorization:
- Use JWT or OAuth to ensure only authorized users can access APIs.
-
Protecting APIs:
- Utilize tokens or secure keys.
- Restrict access to API Routes to prevent brute force attacks.
-
Handling Sensitive Data:
- Encrypt sensitive information before storage.
- Only return necessary data to reduce leakage risks.
Conclusion
With features like SSR, SSG, and API Routes, Next.js provides a comprehensive solution for securing modern web applications. However, it’s essential to combine these features with additional security measures like encryption and authentication to ensure robust data protection.
References
[1]. Muhammad Osama Qaseem. (2024, 08 11). Stars. Retrieved from https://www.pexels.com/photo/stars-27683157/