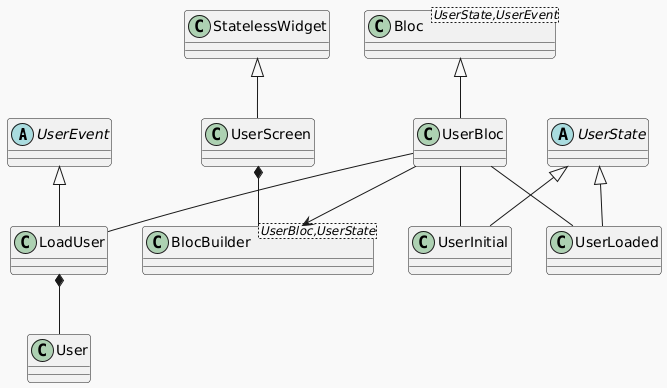
Bloc is come from a unidirectional data flow (UDF) pattern. However, if you want use Bloc in MVVM design pattern, this small post will share with you the way to get it.
The main components in MVVM model:
1. Model (M) :
- Represents your application's data and business logic. Models should be independent of the UI and handle all data-related tasks, such as fetching data from APIs or databases.
2. View (V) :
- Represents the UI of your application. The View subscribes to a Bloc to get updates and display the current state.
3. ViewModel (VM) :
- In Flutter, the Bloc acts as the ViewModel. It holds the state of the UI, handles user input, and updates the state. The ViewModel interacts with the Model to fetch, update, or modify data.
The below small sample app will show how you can structure a Flutter app using Bloc in an MVVM design architecture:
1. Model (M):
- A Dart class that represents your data.
class User {
final String name;
final int age;
User({required this.name, required this.age});
}
2. ViewModel (VM):
- The Bloc will manage the state of the View. It consumed events and emits states.
import 'package:bloc/bloc.dart';
// Events
abstract class UserEvent {}
class LoadUser extends UserEvent {}
// States
abstract class UserState {}
class UserInitial extends UserState {}
class UserLoaded extends UserState {
final User user;
UserLoaded(this.user);
}
// Bloc
class UserBloc extends Bloc<UserEvent, UserState> {
UserBloc() : super(UserInitial()) {
on<LoadUser>((event, emit) {
// Simulate to fetch the user data (from a repository)
final user = User(name: "Teddy Nguyen", age: 44);
//Emit the new event
emit(UserLoaded(user));
});
}
}
3. View (V):
- The UI part that listens to the Bloc for state changes and displays the data.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_bloc/flutter_bloc.dart';
class UserScreen extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('User')),
body: BlocBuilder<UserBloc, UserState>(
builder: (context, state) {
if (state is UserInitial) {
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
} else if (state is UserLoaded) {
return Center(child: Text('Name: ${state.user.name}, Age: ${state.user.age}'));
} else {
return Center(child: Text('Something went wrong!'));
}
},
),
);
}
}
(Feature image designed by rawpixel.com on Freepik)