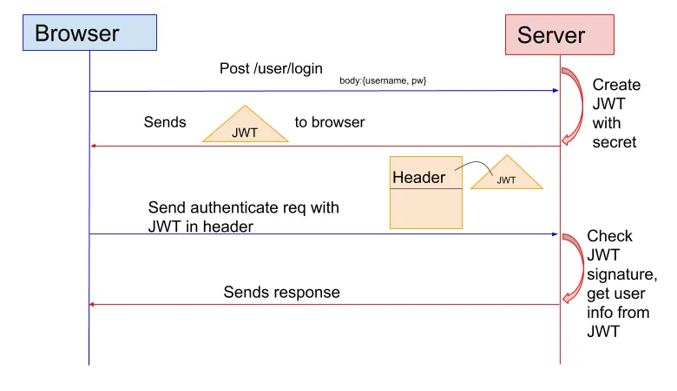
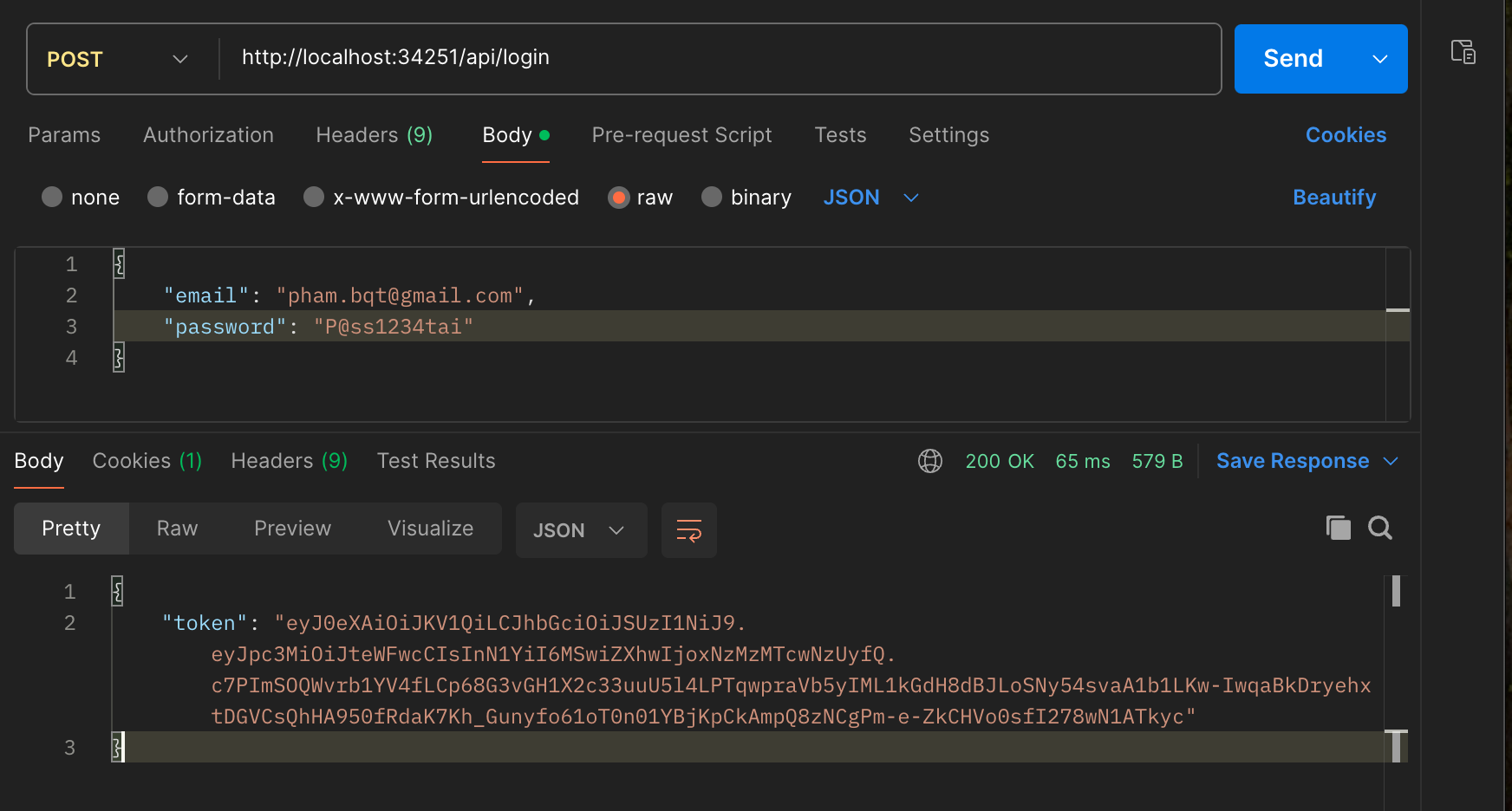
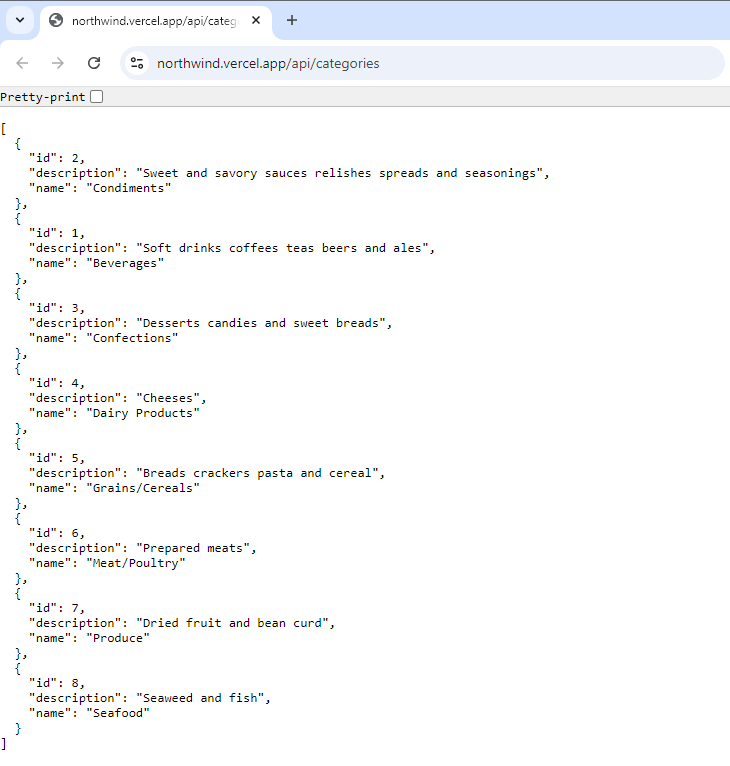
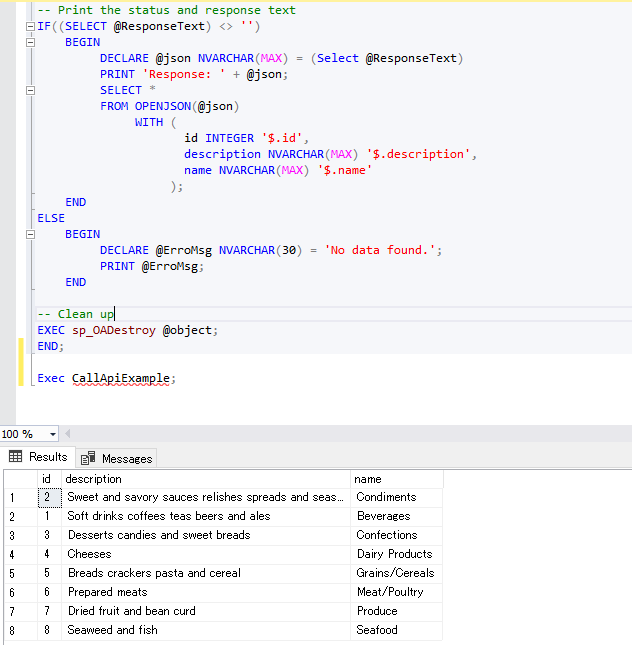
Supabase Overview:
Supabase is an open-source Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) platform that aims to simplify the development process for modern applications. It leverages PostgreSQL as its core database system, which is known for its scalability, flexibility, and feature richness. Supabase offers an easy-to-use interface for developers to quickly build applications without the overhead of managing infrastructure. It is gaining traction worldwide, with a notable presence in markets like North America, Europe, Asia, and South America.
As an open-source alternative to Firebase, Supabase provides features such as authentication, real-time data syncing, file storage, and cloud functions. What makes Supabase stand out is its use of PostgreSQL, allowing developers to access the full power of a relational database while also benefiting from serverless capabilities.
Key Features of Supabase:
- Database: Fully managed PostgreSQL database with an API for fast development.
- Authentication: Secure user management with support for multiple providers.
- Realtime: Built-in real-time updates using WebSockets.
- Edge Functions: Serverless functions that run close to the user for low-latency performance.
- File Storage: Scalable storage solution for managing user files such as images and documents.
- Extensibility: Easy integration with third-party libraries and services.
In summary, Supabase is a powerful solution for developers looking for a fully managed, open-source backend platform that combines the reliability of PostgreSQL with modern tools to simplify application development.
PostgreSQL in Supabase
PostgreSQL powers Supabase and serves as the backbone of the database services. Unlike other BaaS platforms, Supabase allows you to interact directly with the PostgreSQL database, giving developers complete control over their data while benefiting from PostgreSQL's advanced features.
Tools and Features for PostgreSQL in Supabase:
- Auto-Generated APIs: Supabase automatically generates RESTful APIs for your database tables, views, and functions, which eliminates the need for manual backend code.
- Realtime Engine: WebSocket support for streaming changes to your database in real time.
- Authentication Integration: Integrates PostgreSQL with Supabase's authentication service to manage access control securely.
- Dashboard and SQL Editor: A user-friendly interface to manage the database, execute queries, and monitor performance.
- Storage and Edge Functions: Extend PostgreSQL’s functionality with file storage and serverless edge functions.
By providing these tools, Supabase simplifies working with PostgreSQL while retaining all the power and flexibility of the underlying database.
How to use Supabase Database
Supabase Database is a powerful tool that allows you to build and manage databases with ease. Here's an enhanced step-by-step guide to help you get started and implement triggers and functions for advanced functionality.
1. Create a New Project in Supabase:
-
- Start by creating a new project on Supabase
-
- Add the necessary details, such as the project name and region. Please follow the images below.
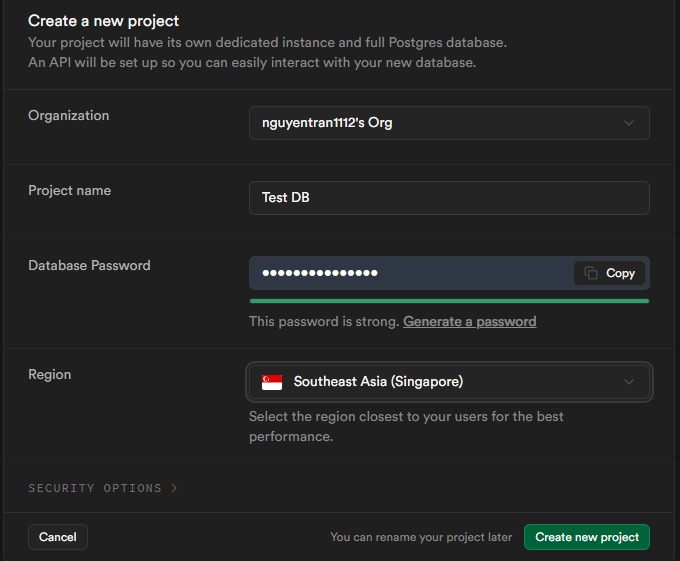
-
- When a project is created successfully, it will display essential information, including security credentials, configuration details, and access guidelines, to ensure proper setup and secure usage.
2. Create Database Tables:
-
- To create the users and orders tables in Supabase, follow the steps below:
- Example queries:
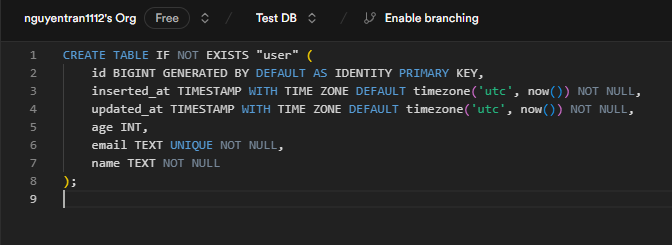
- Create the Users Table: Use the following SQL query to create a users table with essential columns such as user_id, user_name, and other relevant details.
- user_id: A primary key that is automatically generated for each user.
- user_name: The name of the user (required).
- email: The email address of the user, which must be unique.
- age: The age of the user (optional).
-
-
-
- timestamps: The created_at and updated_at fields automatically store the current UTC time for tracking record creation and updates.
-
-
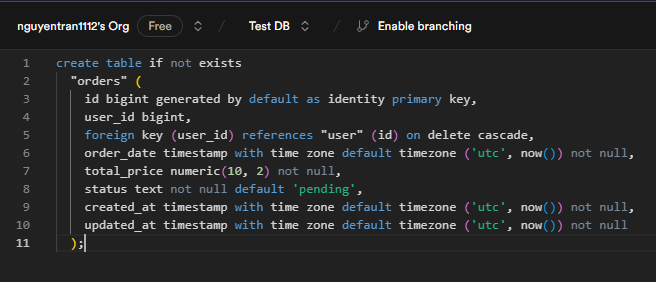
- Create the Orders Table: Next, use this SQL query to create an orders table that will store information about each order, including a foreign key linking it to the users table.
- order_id: A primary key automatically generated for each order.
- user_id: A foreign key referencing the user_id from the users table, establishing a relationship between the two tables. The ON DELETE CASCADE ensures that when a user is deleted, their associated orders are also deleted.
- order date: The date and time when the order was placed, stored in UTC format for consistency.
- total price: The total price of the order, a required field ensuring no order is recorded without a price.
- status: The current status of the order, defaulting to "pending" if not explicitly specified.
- timestamps: The created_at and updated_at fields automatically store the current UTC time for each record, ensuring accurate tracking of record creation and updates.
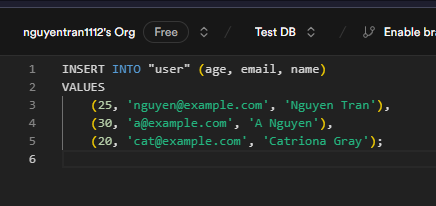
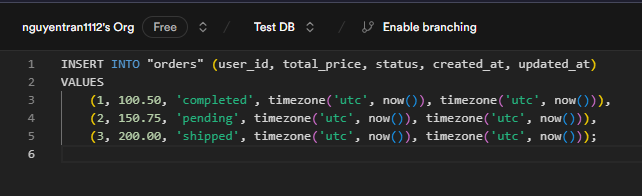
3. Insert sample data: Once the tables are created, you can insert sample data into the users and orders tables.
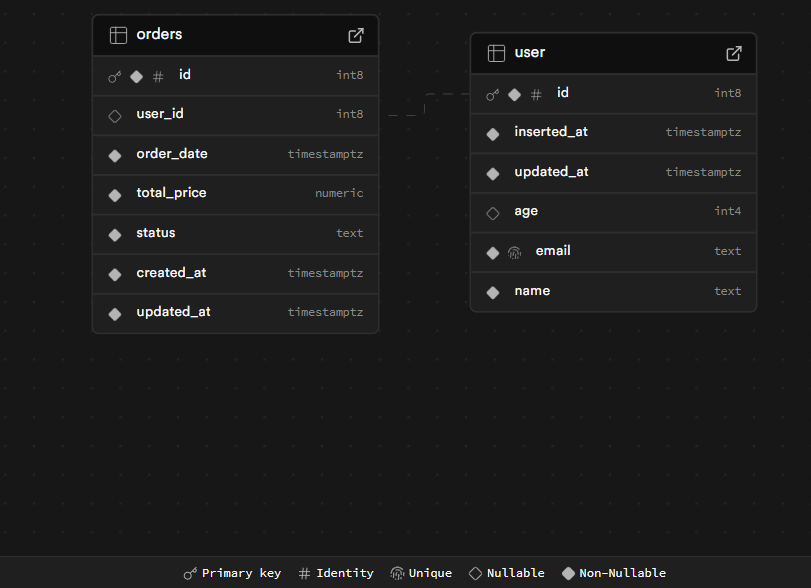
4. Verification: After inserting data, you can query the tables to verify that the records have been added successfully. Supabase provides a powerful Schemas Visualizer and Table Editor to assist developers in managing and visualizing their database schema and structure without the need to manually write complex SQL queries. You can also use these tools to preview the data.
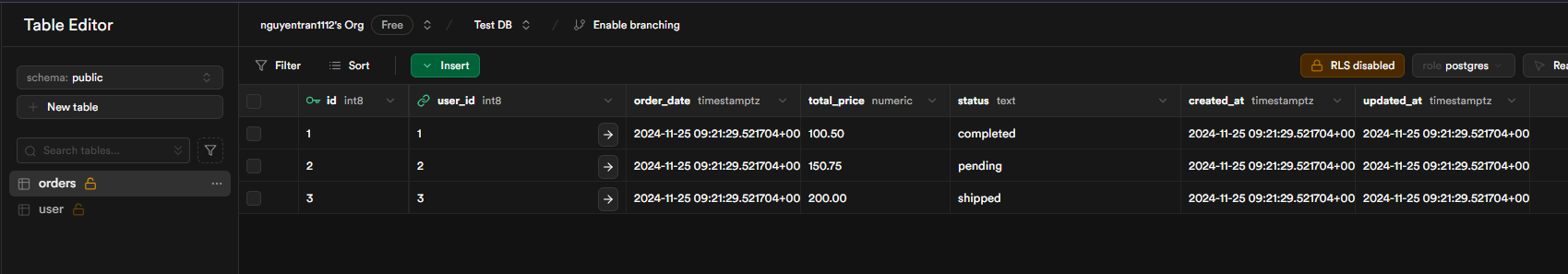
How to Automatically Sync Data Using Supabase Triggers
In serverless environments like Firebase, you often handle business logic on the client side. While this approach works, it can lead to complex client-side code. Supabase, on the other hand, allows you to implement server-side business logic directly in the database using Triggers and Functions. These features enable automatic data synchronization across systems without changing client-side code.
Scenario: Adding User Name to Orders Table
Imagine you have a relational database with users and orders tables, and you want to add the user's name to each order. The goal is to automatically populate the user_name column in the orders table whenever a new order is placed, without requiring any changes to the client-side code.
Example User Story:
Title: View User Name Data in Order Tables
As an operator managing the project,
I want to view the user name data in the order tables,
so that I can easily query and analyze data related to orders and their associated users.
Acceptance Criteria:
- The user_name column is included in the orders table.
- The displayed user name matches the user who placed the order.
- User names are fetched dynamically via a relationship with the users table.
- Operators can filter and sort orders by user name.
- The feature should not degrade performance.
Technical Notes:
- Add a new user_name column to the orders table.
- Use a foreign key relationship between orders and users to populate the user_name field.
Priority: Medium
This feature enhances usability for operators but may not directly impact end-user experience.
Dependencies
- Database schema adjustments for the "Orders" table.
Definition of Done (DoD)
- The "Orders" table includes a "User Name" field populated correctly.
- Operators can filter and query data by user name.
- All unit, integration,... tests pass.
- Documentation updated for the new feature.
Steps for implementing Supabase triggers and functions to fulfill the user story above:
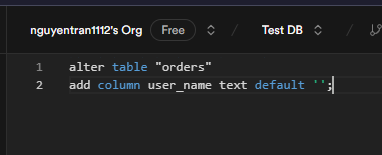
1. Add the user_name column to the orders table:
You can add the user_name column using the following SQL with default value is empty string.
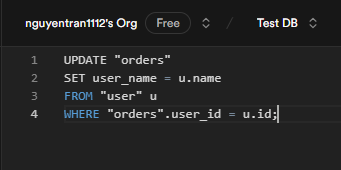
2. Populate the user_name column:
Populate the user_name column by fetching the corresponding name from the users table. You can use an update query:
3. Create a Database Function:
Create a function to insert the user's name into the orders table when a new order is added. This can be done in the Functions section of Supabase.
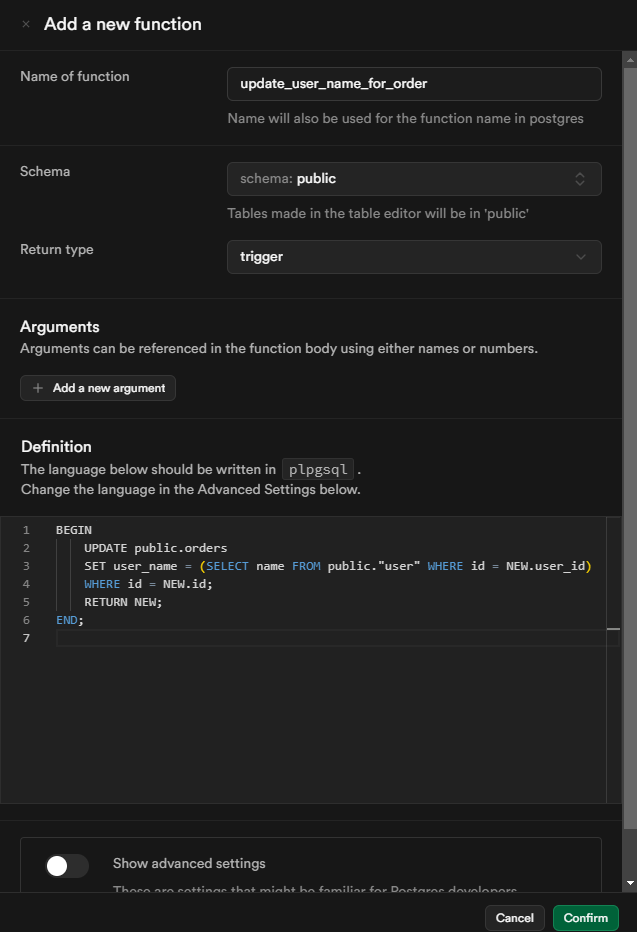
In the Database Management section, please select Functions and then create a new function.
Make sure to complete all the fields in the form to create a new function. This trigger function updates the user_name column in the orders table with the corresponding name from the user table, based on the user_id of the newly inserted order. It ensures that each new order record has the correct user_name associated with it.
4. Create a Trigger to Call the Function:
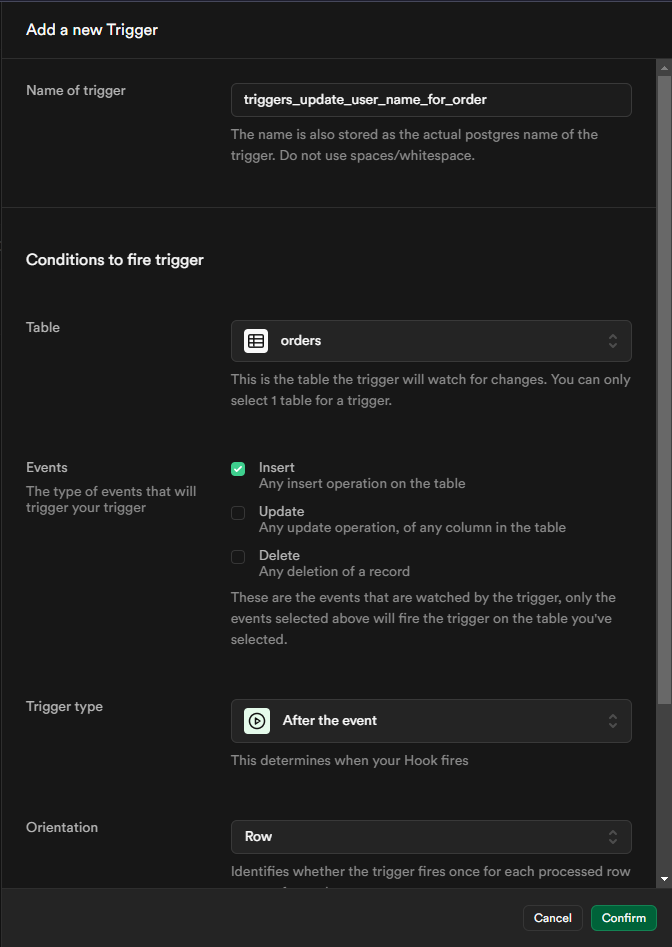
Ensure that you complete all fields in the form accurately when setting up a new trigger. Note that the trigger name should not contain spaces or whitespace. Configuration Details for the Conditions to Fire Trigger section:
-
Table: This is the specific table that the trigger will monitor for changes. It is important to note that a trigger can only be linked to one table at a time. For this task, select the orders table.
-
Events: Specify the type of event that will activate the trigger. For this scenario, choose the event that corresponds to inserting new records into the orders table.
-
Trigger Type:
- AFTER Event: The trigger will activate after the operation has been completed. This is useful for scenarios where you need to ensure that the primary operation has been executed before the trigger runs.
- BEFORE Event: The trigger fires before the operation is attempted. This can be useful for pre-validation or modifying data before the main operation occurs.
-
Operation: The specific operation being monitored in this context is the insertion of new records into the orders table.
-
Orientation:
- Row-Level: The trigger will activate once for each row that is processed.
- Statement-Level: The trigger will activate once per statement, regardless of the number of rows affected.
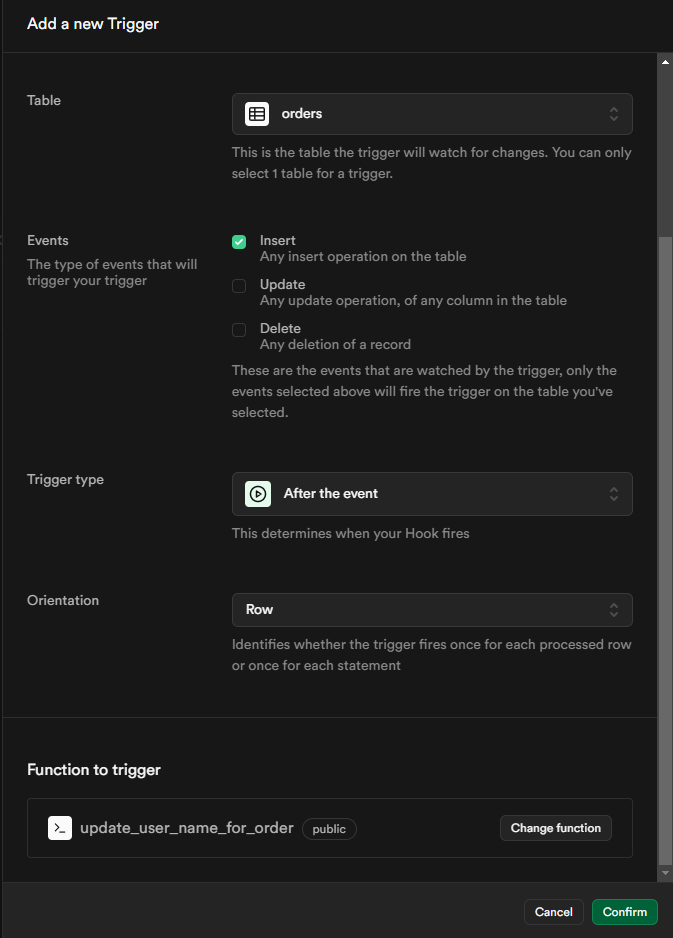
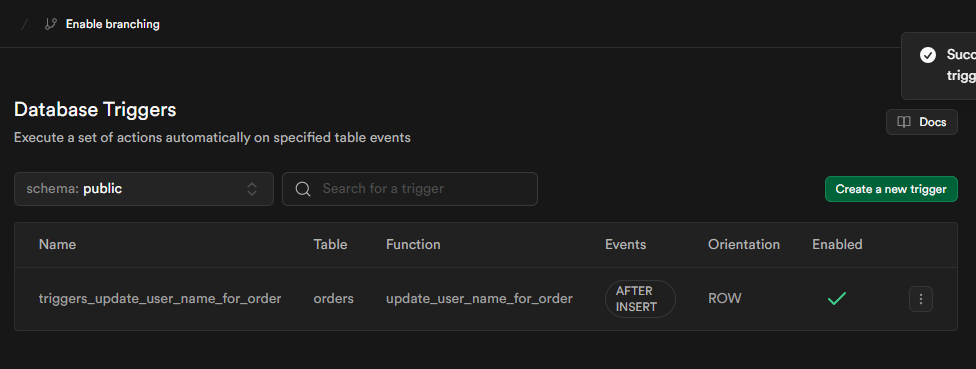
Trigger successfully created, as shown in the image below.
5. Testing
Insert a new record into the orders table and check if the user_name column is populated automatically.
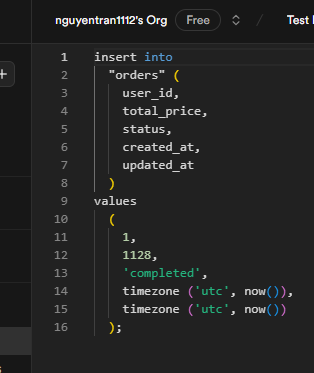
To check if the user_name column is populated after running an insert statement, you can use the following SQL code. This combines the two queries: one to insert a record and another to verify the contents of the last inserted record.
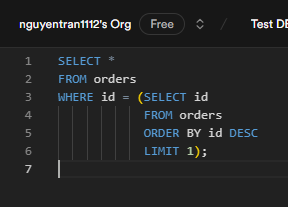
The result of the select statement showed that the user_name column is populated automatically based on the user_id.

Finally, the trigger functions as expected, ensuring that the user story is successfully implemented and completed within the development process.
Conclusion
Supabase provides a powerful and flexible platform for building applications with real-time data synchronization. In this post, we discussed how to use Supabase triggers to automate data updates across systems, enhancing your application's responsiveness and reducing the need for manual data management. We demonstrated how to set up and test triggers to ensure they work as expected, so your data remains consistent and current. By implementing Supabase triggers, developers can focus on building features rather than worrying about data synchronization, leading to a more seamless and efficient development process. This solution makes it easier to manage complex workflows, ensuring that your application scales smoothly and operates efficiently."
Reference
https://supabase.com/